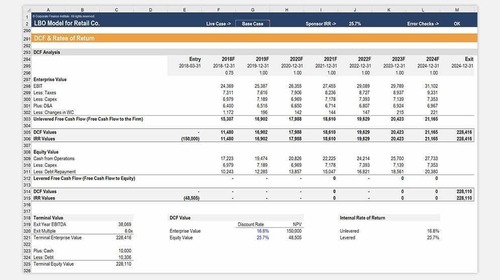
OODA Loop
Observe, Orient, Decide, Act: A rapid, adaptive decision-making framework
Mastering the OODA Loop: A Comprehensive Guide to Decision-Making in Business
In the fast-paced, ever-evolving landscape of business, the ability to make rapid and effective decisions is paramount. One valuable tool that has gained recognition for its efficacy in decision-making is the OODA Loop. Developed by military strategist Colonel John Boyd, the OODA Loop was designed to enhance adaptability, agility, and response in high-stakes, time-sensitive situations.
The OODA Loop is an acronym representing the four essential steps: Observe, Orient, Decide, and Act. John Boyd, a United States Air Force fighter pilot and military strategist, originally created this mental model to describe the cycle of decision-making and action observed in successful combat operations. In creating mental models, Boyd emphasized the significance of adaptability and agility in decision-making, especially in situations where the environment is constantly changing and evolving.
The OODA Loop has been widely embraced in the business world as a method to improve decision-making and navigate the complexities of today’s competitive markets.
Exploring techniques for making rational decisions under pressure involves studying approaches employed in extreme circumstances. If these methods prove successful in the most challenging scenarios, they are likely to be equally effective in more common situations. In this article, we will learn more about this approach and delve into the OODA Loop concept, explore its four steps, examine its advantages and disadvantages, discuss factors influencing its effectiveness, and learn how to apply it in business contexts.
What is the OODA Loop?
While serving as a Colonel in the US Air Force, John Boyd embarked on a quest to unravel the reasons behind the success of his F-86 fighter pilots in their encounters with MiG fighters during the Korean War. His in-depth observations revealed two crucial factors. First, F-86 planes offered a broader field of vision compared to MiG planes. Second, the hydraulic controls of F-86 planes enabled remarkably swift maneuvering, granting pilots a distinct edge in military campaigns.
From these technical insights, Boyd devised a foundational framework that outlined how pilots could secure a competitive advantage in the realm of high-speed conflicts. This initial analysis ultimately served as the cornerstone for what we now recognize as the OODA Loop.
How the OODA Loop Works: The Four Steps
1. Observe
The first step in the four-step process in the OODA Loop is “Observe.” During this phase, individuals or organizations actively collect information and data about their environment. This includes observing market trends, customer feedback, competitor activities, and any other relevant data sources, such as human behavior. The quality and comprehensiveness of the observation significantly impact the effectiveness of the subsequent steps in the OODA Loop.
2. Orient
In the “Orient” step, decision-makers process and make sense of the information gathered during the “Observe” phase. This orientation phase involves assessing the relevance and significance of the data, understanding how it fits into the larger context, and identifying potential opportunities or threats. Orienting oneself effectively is critical for making well-informed decisions.
3. Decide
With a clear orientation step, decision-makers move to the “Decide” step. Here, they evaluate various courses of action based on their assessment and choose the strategy that is most likely to yield the desired results. This approach involves risk assessment, consideration of available resources, and selecting the best approach to achieve the intended objectives.
4. Act
The final step in the OODA Loop is “Act.” In this phase of the feedback loop, the decision-maker takes decisive action by implementing the chosen strategy promptly. The loop then returns to the “Observe” phase, as the outcomes of the action become the new information to be observed and analyzed. The OODA Loop is a continuous, iterative process, with each step in the cycle building on the previous one.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of the OODA Loop?
Advantages
Rapid Response: The OODA Loop, in its simplest form, comprises a systematic information-processing framework. It streamlines and expedites decision-making processes and reaction time, permitting organizations to assess complex situations and generate a response swiftly. The OODA loop is a particularly invaluable tool in tumultuous market conditions, where the demand for quick access to actionable information and the ability to make short-term decisions is paramount.
This agility enables organizations to respond promptly to changing conditions and seize emerging opportunities. In essence, the OODA Loop equips organizations with the capability to navigate a rapidly shifting landscape with precision.
Adaptability: Employing the OODA Loop offers organizations multiple options for adaptation in the face of evolving circumstances. This flexibility makes the organization more resilient in dynamic markets.
The framework’s ability to continually observe, orient, decide, and act empowers adaptability by providing a structured and comprehensive approach to addressing change and uncertainty. It ensures that organizations are not just responsive but also proactive in adjusting their strategies and tactics.
Competitive Edge: In industries marked by relentless and abrupt change, the effective use of the OODA Loop can be a game-changer in competitive strategy. By adhering to this information-processing framework, organizations gain a significant advantage as they consistently outpace rivals in decision-making and action execution.
This enables them to seize opportunities ahead of the competition, respond more effectively to threats, and maintain a dynamic stance in the marketplace. In the complex arena of business competition, the OODA Loop is akin to a strategic compass, ensuring that an organization remains one step ahead.
Disadvantages
Simplicity: The OODA Loop, while valuable, does have its limitations. In its original context as a military strategy concept, it was designed for high-stakes situations, particularly aerial combat, where quick decisions are imperative and not situations experienced in everyday life. In more intricate decision-making scenarios, the OODA Loop may oversimplify matters, potentially neglecting important factors that require more in-depth analysis.
Its simplicity can also lead to a lack of consideration for the nuances and subtleties often present in complex situations such as human behavior, or employee and stakeholder motivation. Decision-makers must be cautious not to rely solely on the OODA Loop when dealing with situations that involve incomplete information or multifaceted dynamics.
Not One-Size-Fits-All: The OODA Loop is a valuable tool, but it is not a universal solution for all types of decisions. Some complex situations, such as those in the fields of healthcare, law, or finance, demand more comprehensive and thorough methodologies. Relying solely on OODA Loops could be inadequate and limiting in these contexts.
As a decision-making tool that emerged from a military environment, the OODA Loop can lead to decision-making that can be too aggressive.
While it excels in situations that require a rapid response to dynamic, unpredictable, and high-stakes scenarios, decision-makers should recognize that its application should be tailored to fit the specific characteristics of the situation at hand. It is essential to have a range of decision-making tools and approaches at one’s disposal to ensure adaptability and effectiveness.
Training Required: To implement the OODA Loop effectively, decision-makers and organizations must invest in training and practice to master this important concept. In high-pressure and extreme situations, the OODA Loop’s effectiveness hinges on individuals and teams being well-versed in its principles and applications as well as its limitations.
Training not only ensures a clear understanding of the OODA Loop but also allows for the development of the necessary skills to make quick, sound decisions. Moreover, it establishes a feedback loop for continuous improvement, enabling individuals and organizations to refine their decision-making processes and adapt them to their unique needs.
Training ensures that decision-makers can navigate the OODA Loop stages with confidence and competence.
What are the Factors that Affect the OODA Loop?
Several factors can influence the effectiveness of the OODA Loop in making decisions.
Information Quality: In the OODA Loop theory, the “Observe” stage serves as the foundation for effective decision-making. The accuracy and reliability of the information gathered during this phase significantly impact the quality of subsequent decisions.
A deep understanding of the situation, encompassing both the nuances and the bigger picture, contributes to the development of a robust mental model. However, it is essential to be aware of cognitive biases that might affect the quality of mental models and observations. Decision-makers must strive for a balanced and unbiased assessment of the data to ensure the integrity of their mental models.
Communication: Efficient communication is not just a state of transmitting information; it’s foundational to the OODA Loop’s effectiveness. Clear and timely communication within an organization is crucial for transmitting decisions and action plans to all relevant parties involved.
Without effective communication channels and practices, even the best decisions can falter during implementation. The “Act” stage hinges on the seamless dissemination process of the initial decision made throughout the organization, ensuring that everyone is aligned with the chosen course of action.
Cultural and Organizational Factors: The success of decision implementation can be greatly influenced by the culture and structure of an organization. Organizational culture shapes how decisions are made and executed. In some cultures, there may be a hierarchical approach to decision-making, while in others, it could be more collaborative.
These cultural norms impact the speed and success of decision implementation. Moreover, the structure of the organization, including the delegation of authority and responsibility, plays a critical role in how efficiently decisions move from the “Decide” stage to the “Act” stage.
Environmental Factors: The external environment plays a significant role in decision-making and the application of the OODA Loop. Market conditions, regulatory changes, geopolitical events, and various external factors can influence the decision-making process.
Decision-makers must be adaptable and ready to adjust their OODA Loop based on changing circumstances. Environmental factors often necessitate recalibrating the “Observe” and “Orient” stages to account for new information and shifting dynamics of the surrounding environment. The ability to recognize and respond to these external influences is an integral part of effective decision-making.
How to Use the OODA Loop in Business
The OODA Loop offers a detailed and structured approach to decision-making that can be effectively applied across various aspects of business operations. Similar to the scientific method, it provides a systematic and iterative process for addressing challenges and opportunities. Here are some areas where it can be particularly beneficial:
Operational Efficiency: Streamlining operations and improving efficiency is a fundamental goal for businesses seeking to reduce costs and enhance productivity. By continuously observing and orienting toward operational data and performance metrics, organizations can identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and opportunities for improvement. Decisions can be made to restructure workflows, automate tasks, or implement new technologies, resulting in a more efficient and cost-effective operation.
Supply Chain Management: Supply chains can be complex and vulnerable to disruptions. Using the OODA Loop, businesses can closely monitor the entire supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivering products to customers. Rapidly observing and orienting to changes in demand, logistics, or geopolitical factors, decision-makers can make informed choices about alternative suppliers, transportation routes, and inventory levels. This agility is crucial for maintaining a resilient and responsive supply chain.
Marketing and Customer Engagement: Marketing strategies require adaptability to meet changing consumer preferences and market dynamics. The OODA Loop can guide marketers in observing trends and customer behavior, orienting campaigns toward target demographics, deciding on the most effective marketing channels, and quickly acting to adjust strategies based on real-time feedback. This approach can help businesses stay competitive and maintain a strong customer base.
Innovation and New Product Development: Businesses that prioritize innovation and product development can leverage the OODA Loop to create a structured process for bringing new products or services to market. Observing emerging market needs and technological advancements, orienting development teams toward consumer demands, deciding on product features, and acting on a well-defined launch strategy can significantly enhance the success of new product introductions.
Competitive Analysis: Staying ahead of competitors is essential in any industry. By continuously observing and orienting toward competitor activities and market changes, businesses can make well-informed decisions on how to position themselves effectively. This may involve adjusting pricing, developing differentiated products, or exploring new market segments. The ability to act swiftly in response to competitive challenges is a strategic advantage.
Human Resources and Talent Management: Human resources departments can employ the OODA Loop to enhance employee recruitment, development, and retention. Observing the job market, orienting hiring strategies to attract top talent, deciding on training and development programs, and acting on performance feedback can create a more agile and adaptive workforce.
Financial Management: Financial decision-making requires careful observation and orientation to market trends, economic conditions, and internal financial data. The OODA Loop can guide organizations in making well-informed decisions regarding investments, budget allocations, and risk management. The ability to act quickly in response to market fluctuations is essential for maintaining financial stability.
Customer Support and Service: Exceptional customer service is a competitive advantage. The OODA Loop can assist in continuously observing customer feedback and issues, orienting support teams to customer needs, deciding on service improvements, and taking immediate action to resolve problems and enhance the customer experience.
In all these areas, the OODA Loop fosters adaptability, responsiveness, and informed decision-making. It empowers businesses to thrive in dynamic and competitive environments. However, it’s important to recognize that the OODA Loop is not the only framework for decision-making, and in some situations, alternative methods may be more suitable such as Ethical Decision Making, using a Decision Tree, or Plan-Do-Check-Act.
Summary
The OODA Loop is a versatile tool that transcends its military origins, offering a structured and adaptable framework for addressing the dynamic challenges and opportunities that businesses encounter. Its systematic approach to decision-making aligns well with the demands of today’s ever-changing business landscape.
Additional Resources
Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in